

A long pushing stage during birth (over one hour).Cesarean section (it is unclear whether this is due to the stress of surgery, medications, delaying breastfeeding, and/or less than optimal breastfeeding management).Stressful, exhausting, or traumatic vaginal birth.Pain medications during labor, regardless of delivery method.First time mothers – tend to have milk come in about a day later than mothers with more than one child.Studies have shown that risk factors for delayed onset of lactation include: When a mother’s milk does not undergo the expected increase in volume within 3 days of birth (72 hours postpartum) – this is called delayed onset of lactation (DOL). Risk factors for delayed onset of lactation Skin-to-skin contact with baby has also been associated with increased milk production. Milk production will begin to shut down if milk is not being removed by the time your milk is coming in. However, mothers who breastfeed early and often (or express milk if breastfeeding is not going well) have higher milk production on days 3-4, and their infants lose less weight and have lower bilirubin levels (less jaundice). Keep in mind that many women experience their milk coming in as a gradual change, rather than a sudden one. Research indicates that this timing is hormonally controlled – it does not require that baby be breastfeeding at all. if you’re expressing milk or leaking, you may notice the milk begin its gradual change in appearance from the thicker golden colostrum to the thinner, whiter mature milk.change in baby’s feeding patterns and behavior at the breast.breast fullness, swelling, heaviness, warmth, engorgement, tingling.Signs that your milk is increasing may include:
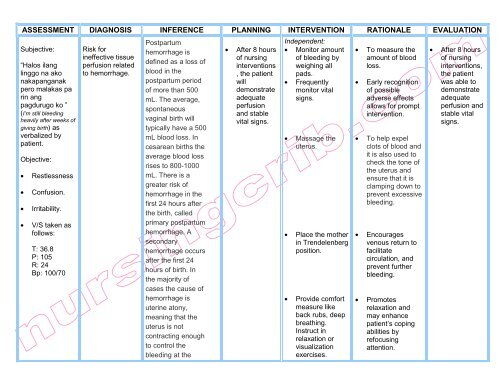
#Retained placental fragments full#
Milk “coming in” generally refers to the time when the mother notices increased breast fullness (and other signs) as milk production begins to kick into full gear– this usually occurs 2-3 days after birth, but in as many as 25% of mothers this may take longer than 3 days. Milk production normally begins to increase (biochemically) between 30 and 40 hours after delivery of the placenta, but it may take a little while for the changes to become apparent to the mother.
References: ABM 2009, Mannel et al 2013, Mohrbacher 2010.
#Retained placental fragments code#
Use PRC code “KELLY” for a special discount!Īverage Intake of Colostrum/Milk Baby’s Age


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
